Login

Login

Dec. 08, 2025
Conveyor belts are one of the most fundamental components in modern material handling. From mining and manufacturing to logistics, food processing, and airports, conveyor systems keep industries moving efficiently.
Despite their wide usage, selecting the right conveyor belt is rarely simple. Buyers, engineers, and operators tend to ask the same core questions again and again—because choosing the wrong belt can lead to downtime, excessive maintenance, and unexpected costs.
Below are the five most common questions people ask when evaluating conveyor belts, along with clear and practical answers.
This is usually the first and most important question. Conveyor belts are not interchangeable—different applications require different belt materials and structures.
Common conveyor belt types include:
Rubber conveyor belts for heavy-duty and abrasive materials
PVC or PU conveyor belts for food processing and hygiene-sensitive environments
Modular plastic belts for easy maintenance and frequent washdowns
Fabric conveyor belts for light to medium loads
Steel cord belts for long-distance and high-tension conveying
Choosing the right belt depends on factors such as load weight, operating environment, temperature, incline, speed, and hygiene requirements. Matching the belt type to the application is critical for performance and lifespan.
Conveyor belt lifespan varies widely and depends more on usage conditions than on the belt itself.
Key factors affecting belt life include:
Load weight and impact at transfer points
Material abrasiveness
Belt speed and operating tension
Environmental conditions (heat, moisture, chemicals, dust)
Maintenance quality and belt alignment
In light-duty applications, a conveyor belt may last many years. In harsh or heavy-duty environments, belts wear faster and require regular inspection and periodic replacement. Proper installation and preventive maintenance significantly extend belt life.
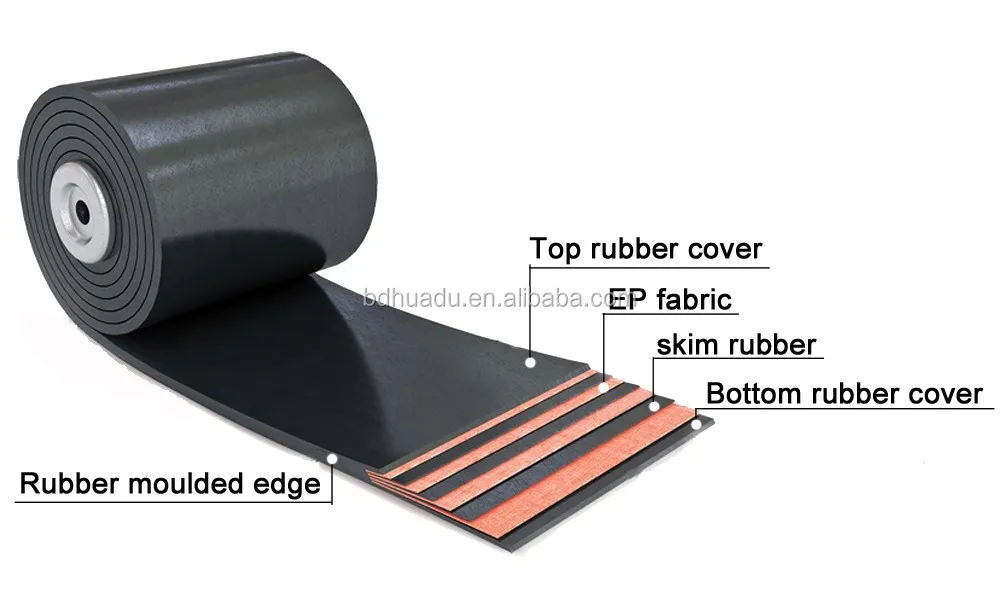
Many conveyor belt failures are preventable and result from system-related issues rather than defects in the belt material.
Common causes include:
Misalignment and poor tracking, leading to edge wear and damage
Excessive tension, causing stretching or internal reinforcement failure
Material buildup on rollers and pulleys
Improper loading, such as dropping material from excessive height
Inadequate maintenance, including worn idlers or seized rollers
Addressing these issues early helps avoid unexpected shutdowns and costly production losses.
Maintenance requirements depend heavily on belt type, application, and environment.
Typical conveyor belt maintenance tasks include:
Regular visual inspection for wear, cuts, or fraying
Checking belt tracking and adjusting alignment
Cleaning material buildup from the belt and rollers
Monitoring belt tension and splice condition
Replacing damaged components such as idlers or scrapers
Modern conveyor belts and automated systems can reduce maintenance needs, but no conveyor belt is truly maintenance-free. A scheduled preventive maintenance plan is essential for reliable operation.
Buyers often focus on initial price, but conveyor belts should be evaluated based on total cost of ownership, not just purchase cost.
Lower-priced belts may result in:
Shorter service life
Higher maintenance frequency
Increased downtime
Reduced efficiency
Higher-quality belts typically cost more upfront but offer better durability, energy efficiency, and reliability. The right balance depends on production volume, criticality of uptime, and operating conditions.
For most operations, investing in a belt that meets performance requirements and reduces operational risk delivers better long-term value.
Conveyor belts may appear simple, but their impact on productivity, safety, and operating costs is significant. The most common questions people ask—about belt type, lifespan, failure causes, maintenance, and cost—highlight the importance of informed selection and proper system design.
By understanding these key considerations and choosing the conveyor belt that truly fits the application, businesses can reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and extend the life of their conveyor systems.
28 0 0
Join Us

Comments
All Comments ( 0 )